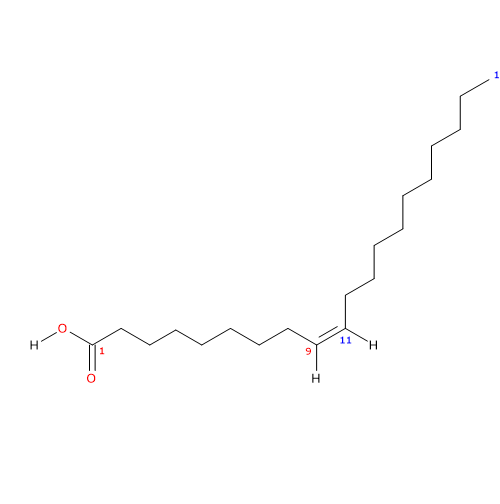
Gadoleic acid, a carboxylic acid with a 20 carbon chain, was discovered in cod liver oil by Bull H. in 1906, while the structure was clarified by Takano M. in 1933.
It belongs to the group of unsaturated fatty acids. It has one cis double bond, from the methyl end in omega-11 (ω-11) or n-11 position, so in shorthand is 20:1n-11. It is member of the sub-group called very long chain fatty acids or LCFA, namely, fatty acids with 20 or more carbon atoms.
PROPERTIES
Molecular weight: 310.51452 g/mol
Molecular formula: C20H38O2
IUPAC name: (Z)-icos-9-enoic acid
PubChem: 5282767
In purified form, its melting point is at 23-23.5 °C (73.4-74.3 °F; 296.15-296.65 K) and boiling point at 170 °C (338 °F; 443.15 K) at 0.1 mmHg.
OTHER NAMES
cis-gadoleic acid
9Z-eicosenoic acid
cis-9-icosenoic acid
cis-9-eicosenoic acid
20:1n-11
Food sources of gadoleic acid
It occurs as glycerol ester in fish (where it originates from dietary crustacean) like cod, shark and ray or their liver oils, and vegetable oils like this from rapeseed.
References
- Akoh C.C. and Min D.B. “Food lipids: chemistry, nutrition, and biotechnology” 3th ed. 2008
- Chow Ching K. “Fatty acids in foods and their health implication” 3th ed. 2008