Nervonic acid (24 carbon atoms) was first discovered by Tsujimoto M. in 1927 in fats of Elasmobranch fishes, a subclass of Condroitti class including fishes with fusiform (selachii like sharks from with its first name selacholeic acid) or flatten (batoidea like ray) bodies.
Its structure was established in the same year by Klenk E. who isolated it from cerebrosides of brain tissue.
It belongs to the group of unsaturated fatty acids (one cis double bond, from the methyl end is in omega-9 (ω-9) or n-9, so in shorthand is named 24:1n-9) member of the sub-group called very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA), from 20 carbon atoms onwards.
PROPERTIES
Molecular weight: 366.62084 g/mol
Molecular formula: C24H46O2
IUPAC name: (Z)-tetracos-15-enoic acid
PubChem: 5281120
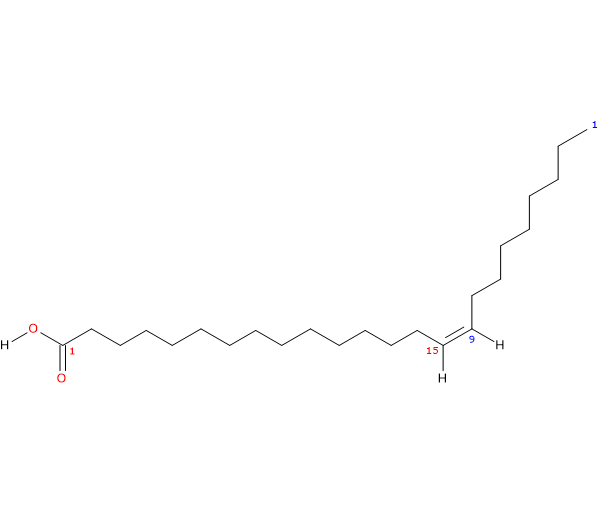
In purified form, it is a clear to yellowish crystalline powder insoluble in water with melting point at 42.5-43 °C (108.5-109.4 °F; 315.65-316.15 K).
OTHER NAMES
selacholeic acid
cis-15-tetracosenoic acid
(15Z)-tetracosenoic acid
(Z)-15-tetracosenoic acid
(15Z)-tetracos-15-enoic acid
cis-delta(15)-tetracosenoic acid
24:1n-9
Synthesis of nervonic acid
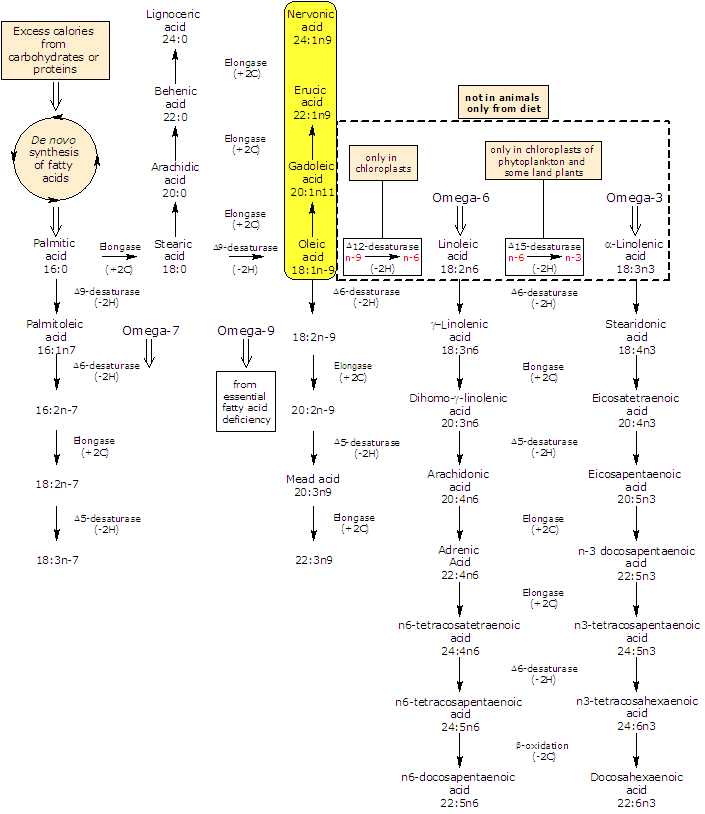
It is produced from oleic acid, that undergoes three consecutive chain elongation steps, catalyzed by elongases.
Two carbon units are added in each step, with production of gadoleic acid, erucic acid, and finally, nervonic acid.
Selacholeic acid and myelin
It is important in the biosynthesis of nerve cell myelin.
In the human brain, nervonic acid and lignoceric acid make up 60% of the fatty acids of sphingomyelin of white matter (lignoceric acid is a saturated fatty acid which consists of 24 carbon atoms).
Food sources of nervonic acid
It occurs as glycerol ester in fish oil like liver oil of spiny dogfish shark (Centrophorus granulosus) and in high amounts (22-25%) in Lunaria annua, a plant of the family of Brassicaceae, synonym Cruciferae.
References
- Akoh C.C. and Min D.B. “Food lipids: chemistry, nutrition, and biotechnology” 3th ed. 2008
- Chow Ching K. “Fatty acids in foods and their health implication” 3th ed. 2008