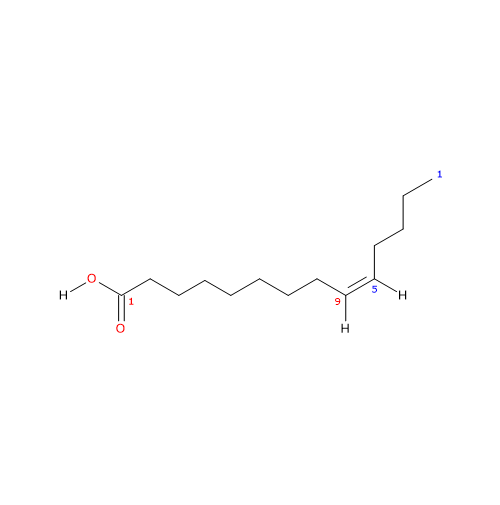
Myristoleic acid (14 carbon atoms) belongs to the group of unsaturated fatty acids, having a cis double bond, from the methyl end, in omega-5 (ω-5) or n-5 position. So, in shorthand is named 14:1n-5. It is also a member of the sub-group called long chain fatty acids or LCA (from 14 to 18 carbon atoms).
PROPERTIES
Molecular weight: 226.35504 g/mol
Molecular formula: C14H26O2
IUPAC name: (Z)-tetradec-9-enoic acid
PubChem: 5281119
In purified form its melting point is at -4 °C (24.8 °F; 269.15 K).
OTHER NAMES
- 9-tetradecenoic acid
- (9Z)-tetradecenoic acid
- cis-delta(9)-tetradecenoic acid
- 14:1n-5
Food sources of myristoleic acid
It occurs as glycerol ester in animal fats.
It is also found in some non-edible vegetable oils; in fact, as the corresponding saturated fatty acid, myristic acid, is one of the main components of seed oils derived from plants of the genus Myristicaceae (in some species up to 30 percent of the oil; however, myristic acid is present in larger amounts).
It is found in a few foods, and in most cases, in very low quantities.
It is present in small amounts in meat from cattle, horse, chicken and turkey, with a highest value in the brisket of adult cattle, 0.32 g/100 g of edible portion. It is absent in pork. It is also found in whale’s blubber, and turtle fat.
It is absent in almost all processed and preserved meats, such as cold cuts and sausages. Small amounts are present in the cured raw beef (Bresaola), 0.01 g/100 g of edible portion, and in some types of salami, 0.02 g/100 g of edible portion, while the highest value is found in suet, 0.5 g/100 g of edible portion. It is absent in lard.
In dairy products, it is present:
- in very small amounts in milk and yogurt;
- in larger amounts in cream, 0.31 g/100 g of edible portion;
- but, butter is the food which contains the highest amount in absolute terms, 1.14 g / 100 g of edible portion;
- it is absent in most of seasoned
It is absent in eggs.
It is virtually absent in all fishes, excluding sturgeon where it is present in very small amounts, 0.01 g/100 g of edible portion, eel fillet, 0.18 g/100 g of edible portion, and shark liver.
It is absent in edible vegetable fats and oils, including margarine.
It is not found in cereals and derived flours, legumes, and fruit.
References
- Akoh C.C. and Min D.B. “Food lipids: chemistry, nutrition, and biotechnology” 3th ed. 2008
- Chow Ching K. “Fatty acids in foods and their health implication” 3th ed. 2008